
Life Expectancy For Retirement Planning
- RetireOn
- Updated: March 13, 2024
Do you know how long you will live?
It’s a sombre question, I know. But it’s also an important one. There’s a lot riding on the answer.
Whilst there’s no way of getting a definitive number, there are reliable, data-driven factors that can help you make a realistic prediction. This can be very important when considering your retirement planning goals.
Find out how you can estimate your life expectancy in this post.
Video Learning
Global Overview
The World Health Organisation published a map in 2016 that shows worldwide life expectancy rates for both genders at birth.
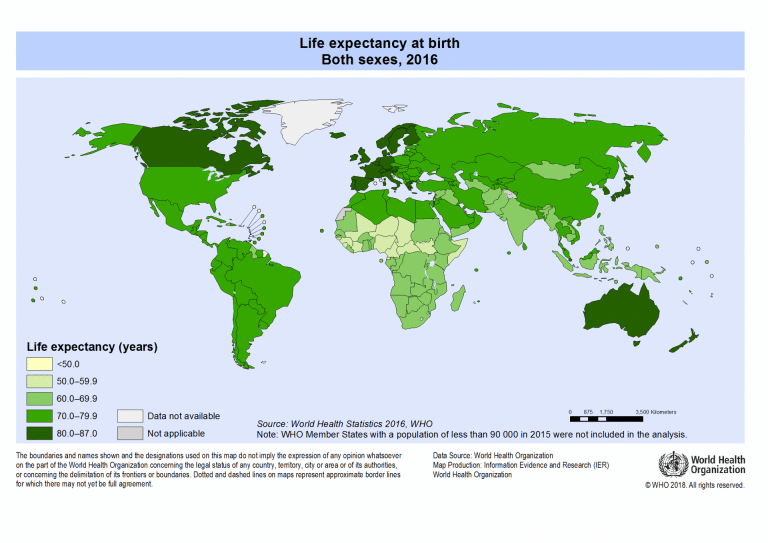
As you can see, the dark green regions such as Australia, Canada and western Europe have the longest life expectancy, in the range of 80-87 years. At the other end of the scale in light green, central African countries have a life expectancy of around 50-59 years.
Let’s take a closer look at some specific examples, from the US and Australia.
Life Expectancy in USA
According to the US Social Security Administration, an American man turning 65 in 2018 can expect to live, on average, until 84. A woman of the same age in 2018 can expect to live, on average, until 86.
I recommend you to use the life expectancy calculator from the Social Security website, in order to estimate your life expectancy considering your age and gender.
Life Expectancy in Australia
According to the Australian Institute of Health and Welfare (2018), a man born between 1960 and 1962 can expect to live, on average, until 67. A woman born between those years can expect to live, on average, until 74. These ages, however, vary significantly according to many factors.
Please read the Age Factor in the next section, in order to find out how Australian ladies are expected to live until 89 years old.
Life expectancy at birth in Australia has risen steadily over time. In 2016, life expectancy at birth was 80.4 years for males and 84.6 years for females.
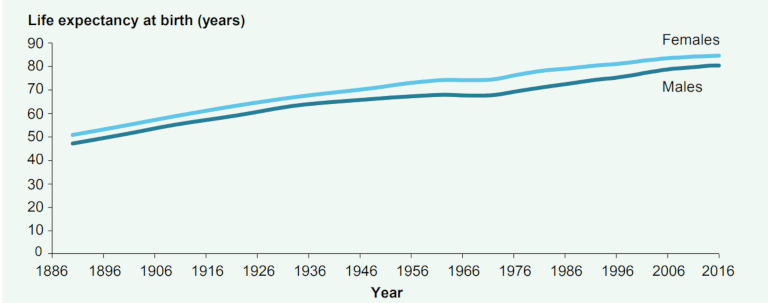
It is also worth looking into the detail on how life expectancy changes along with the health conditions. The data and graph are from the same source – Australian Institute of Health and Welfare.
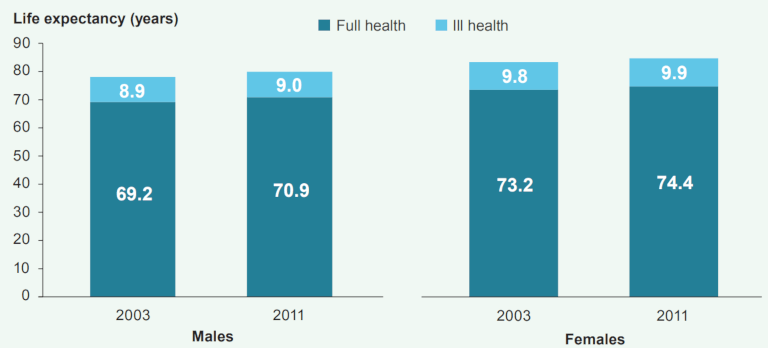
So far, all of these statistics are based purely on gender and date of birth. However, there are a range of factors that can influence your life expectancy. Let’s take a closer look at some of them.
Factors Influencing Life Expectancy
There are 10 main factors worth exploring.
Factor 1 – Gender
Firstly, there is gender. As most people know, men have a lower life expectancy than women. A possible reason for this is that men are more likely to die from injuries acquired through work, war, accidents or suicide. It’s also thought that women are more resistant to infections and degenerative diseases than men.
Factor 2 – Health
Secondly, there is health. We all know what a healthy life entails. But how many of us follow through on the expert’s advice? It’s an important question, because making consistent, healthy choices can have a significant impact on your life expectancy.
Two of the main barriers to healthy living are smoking and alcohol consumption. Limit or eradicate these habits from your life, and you’ll make a dramatic boost to your life expectancy.
Factor 3 – Education
The third influencing factor is education. Generally speaking, the better educated you are, the more likely you are to be aware of risky and dangerous behaviours, and to avoid them.
In addition, your level of education directly influences the nature of your employment, your salary, and whether or not you can afford medical treatment.
Factor 4 – Housing
Fourth, there is housing. Better quality housing is associated with higher life expectancy. This may not be a standalone factor however, since housing is directly related to income, employment and education.
Factor 5 – Climate
Along with housing, there is the role of climate. Living in a warm, humid climate reduces your life expectancy because bacteria thrive in such conditions. As such, you are more likely to get infected with a bacterial disease.
Factor 6 – Genetics
The fifth contributing factor is genetics. Simply put, there are a range of inherited genetic conditions that can impact your life expectancy. There’s not much you can do about such conditions, however, thankfully this is not considered a major contributing factor.
Factor 7 – Occupation
Next up, we have occupation. It’s important to have a secure job with a decent salary. It’s also important that the work is meaningful, and leaves you sufficient time for rest and play.
Factor 8 – Medical Care
There is also medical care. Health services can vary greatly across the globe. Countries that have better quality medical facilities and ready access to doctors generally have much higher life expectancies.
Factor 9 – Political and Social Stability
The ninth influencing factor is political and social stability. Living in a safe, stable environment increases your quality of life and means you are less likely to suffer at the hands of violence.
Factor 10 – Age
And lastly, there is your age. As strange as it may sound, the older you are, the higher your life expectancy will be.
There are three stages of life when you are at a high risk of dying. The first is at birth, when you are vulnerable and dependent on caregivers. The second stage is your late teens and early twenties. This is a time of high-risk behaviour. The third stage is old age when you are infirm and in need of assistance.
If you make it through these three stages, your life expectancy jumps considerably.
By way of example, an Australian woman who is 80 years old in 2002 will have another 9.9 years to live on average, making her life expectancy 89.9. If she makes it to 85, she now has another 7 years to live. This bumps her life expectancy up to 92.
Now let’s say she makes it to 90 in 2012. This will add another 4.8 years to her life expectancy, taking it to the ripe old age of 94.8.
So as you can see, the older you get, the longer you can expect to live. The results are similar for men, and similar throughout other western countries such as the US, Canada and the UK.
Life Expectancy for Retirement Planning
They say knowledge is power. Understanding the key factors influencing life expectancy is the best way to ensure you live a long, healthy life. It’s also crucial for accurate, realistic retirement planning.
It’s important to err on the side of optimism and plan for the best-case scenario. Assume you will live a long life. Which means a long retirement. And that means ensuring you have the right financial support in place.
According to the Retirement Standard report by the Association of Superannuation Funds of Australia (ASFA), a couple aged around 65 needs a budget of A$60,977 per year, in order to support a comfortable lifestyle.
It might shock you to know that this equates to more than half a million dollars over 10 years of retirement. That’s a lot of money, and it will take sound financial planning to get there.
But don’t be discouraged. There are many things you can do to improve your financial situation and plan for a long and comfortable retirement. And it’s never too late to start.
Check out our huge range of videos and articles here at RetireOn, to help you make the most of your golden years. Please subscribe to our YouTube Channel and our newsletter if you want to be notified when a new video or a post is released. You can also find us on Facebook.










